Corona virus : societies and
states
Psychology of individuals and the state's crisis management
Psychology of individuals and the state's crisis management
Dr
Belgacemi Mouloud
Researcher in international
studies
Introduction :
The US Secretary of Defense in cold war
said : « The era of strategy has ended
and a new era has begun called the era of crisis management ».
With the spread of the Corona virus in the world and the increase in the number of infected peopl , societies and states were divided into two parts: societies and countries
that possess scientific knowledge and traditions and
possess institutions with a strategic vision and a scientific method in management and organization, and others waiting for their inevitable fate to live in populism and
chaos and manifestations of
backwardness and failure, and find societies around the world itself facing a crisis imposed by the authorized at the stage of the experience and challenge the behavior of society, culture and capabilities of institutional if we start in the analysis of that state
as the most prestigious social organization, and thus regulated
conduct is not like the rest of the traditional organizations, but
must have a comprehensive strategy rational and contains a set of sectoral
strategies and within her feed strategy of risk management and crisis and their ability to adapt and
deal with risks and crises of the environnement strategy.
The concepts
used in this paper the concept of crisis,
which refers to an unusual condition that leads to the negative results of an unexpected
inability of the Organization or the State to achieve its objectives set out in
time and can be defined as a threat and danger to goals, values and beliefs of
societies, organizations and countries
I. Corona virus and the psychology of societies :
Indicates « Laurent-Henry Venue » That
epidemics are a common product of nature and
societies, between microbes and humans , and germs only become dangerous in certain circumstances and as a result of human intervention.
In terms of social behavior of individuals, the spread of the Corona
epidemic has created a minimum distance between people and thus the dissolution
of some human relations. Wearing a face mask differs in its philosophy among
societies, which is considered by some Asian cultures to be an ordinary matter
unlike Western societies that consider it a kind of selfishness for fear of
Transmission of the epidemic, also some health and social habits of some
societies encourage the spread of the epidemic and hinder the application of
crisis management procedures.
Within the framework of the psychology of individuals and the impact of
epidemics on societies where everyone warns of everyone and began unfamiliar scenes of selfishness,
defending stores and trying to race with time to store everything , and a more
dangerous condition of the spread of the virus Fear of the future and doubting
anything, which is similar to the psychology of wars .
Epidemics throughout history, especially the Corona virus, have produced
new concepts such as quarantine and universal sterilization that have changed
our health systems - is if some underdeveloped societies have a health system -
as indicated by the historian and demographic expert. »Patrice Bordeaux « From
the Graduate School of Science and social , and that topic of epidemics have a
structural impact on the history of health in communities, and the experience
of countries with epidemics especially that have the capacity to the learned
from their experiences produced a state of perception of the existence of a
strategy for risk and crisis management, and orientation Towards a new
generation of experts in the viruses and in the field of risk and crisis
management, as indicated by the French geographer "Freddy Fennet".
Therefore, the Corona pandemic crisis can be an opportunity to reconsider
our social and culture through educational methode, and although the spread of
the virus outside China has been rapid, many societies and countries have been
able to prepare and plan by synergizing civil society efforts and
organizational capabilities in mobilizing society And his preparation, in
addition to the strength of the state institutions and traditions at work with
a strategic vision for crisis management.
As for societies which was not prepared to face risks and crises, the
social culture and the behavior of its members hinder the application of any
crisis management strategy, and for this kind of societies must reconsider
relationship with its scientific research to had taken precautionary measures
to curb the spread of the epidemic.
II. Fragile societies and the absence of a crisis management strategy:
The concept of crisis management is a relatively
recent concept in terms of revitalizing them as a branch of science management
and organization and is difficult to find a precise concept, it can be defined
as the set of processes that seek to overcome the crisis, avoid its negatives
and benefit from its positives, also require crisis management philosophy be a
perception of the crisis and perception is not only by having information and a
team of specialists to analyze, as indicated by the researcher « Dr.
Merbah Malika » in her book, "Crisis Management Strategy and
Governance Effectiveness.", the Crisis Management Team must be aware of
the nature of crisis and its precise description, and know its causes and the
capabilities required to deal with it and the available capabilities and the
time required to deal with it, the
crisis represents a threat to an organization, a state or societies , and the
crisis needs an approach to work to avoid strikes and transfer them from losses
to achieve positive elements and benefit from them, and risk and crisis
management stems from a strategic vision and not from randomness decisions .
One of the indicators of measuring the strength of the state is its health
system, and the ability of its institutions to manage risks and crises
societies did not believe that the proliferation of China would be this
strong, even European countries were not ready to face this virus, due to
the nature of the health system in these countries, as for many countries, they
face structural failure and the absence of a strategic crisis management
strategy, and their organization remains dependent on improvised reactions and decisions
at the expense of having a comprehensive strategic vision.
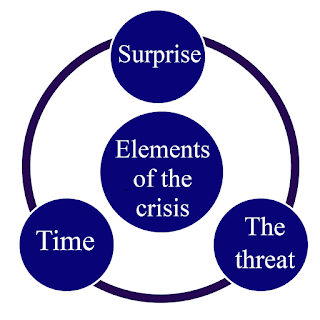
Especially since the nature of modern crises contains an element of
surprise that cannot be expected in terms of space and time, and it
represents a threat to the present and the future, moreover, these crises
represent a turning point that imposes actions and reactions to face emergency
situations; it is characterized by ambiguity, and it is difficult to make a
decision in the changing environment and avoid mistakes because there is no time
to fix the error.
figure
explain elements of crisis characteristics
Figure
prepared by the researcher
On the societal aspect of crisis management through
the role of institutions between efficiency and inefficiency, crises determine
the history and fate of societies, and history proves that societies and
countries that relied on an effective strategic and policy vision based on
scientific thinking were more capable of sustaining themselves than societies
and countries that deal with crises and risks populist and chaotic away from
scientific thinking.
And whoever argues that the Corona virus was a surprise for countries
dealing with it for the first time, even China is facing this epidemic for the
first time like other countries, but its organizational capabilities have made
it a model in managing risks and crises, many countries have dealt with Corona
virus recklessly, in addition to the fragility of their health system and the
absence of a strategic vision, and the absence of awareness that the epidemic
crisis is related to health security and therefore one of the levels of
national security of countries and therefore it must be dealt with according to
the national security approach.
Finally, many societies must take advantage of this crisis because it is an
opportunity to learn, they must reconsider their philosophy of management and
organization, and formal institutions have a strategic vision and philosophy in
crisis management, it is not possible for societies and states to turn to
science and scientific thinking. We find some societies and states, especially
Arab, deal in a traditional way, especially that our institutions suffer from
many problems, including their ability to perform and thus their ability to
manage crises.
Societies and their intellectuals must also be more understanding and aware
of the size of responsibility towards their countries and not deal with risks
and crises outside the human security approach.




0 تعليقات